Dec 23, 2023
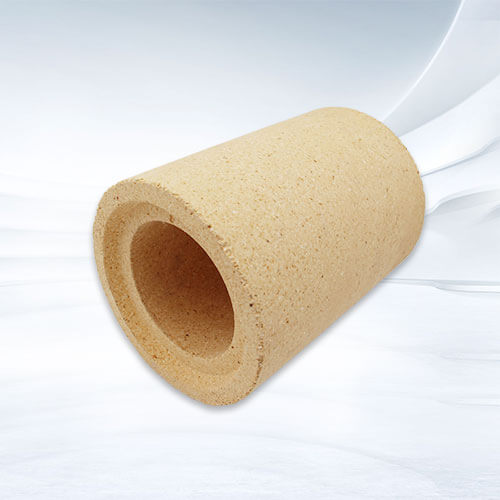
Are Chrome Corundum Bricks Expensive? How Much Does per Ton Cost?
Chrome corundum brick uses Al2O3 as raw material, adds an appropriate amount of chromium oxide powder and chromium corundum clinker fine powder, and is shaped and fired at high temperatures. The chromium oxide content of sintered chromium corundum bricks is generally lower than that of fused chromium corundum bricks. It can also be prepared by the mud casting method. α-Al2O3 powder and chromium oxide powder are evenly mixed, and a debonding agent and an organic binder are added to form a thick mud. At the same time, part of the chromium corundum clinker is added, and bricks are made into bricks by grouting, and then fired. It can be used as glass kiln lining, brushed glass flow hole cover brick, and used in molten iron pretreatment devices, garbage incinerators, coal water slurry pressurized gasification furnace backing, etc.
Currently, the application of chrome corundum bricks has a wider range of applications. One is chromium corundum brick made of metal chromium slag as the main raw material. This product is widely used in zinc smelting electric furnaces and volatilization kilns. Chromium corundum bricks have good thermal vibration stability and high-temperature creep properties. At the same time, it meets the requirements of the circular economy.

Application and Development of Chrome Corundum Bricks
Based on the good corrosion resistance and thermal shock resistance of chromium corundum bricks. The promotion and application of chromium corundum materials will effectively extend the operating life of pool furnaces and produce long-term economic benefits.
Use chrome corundum bricks to make kiln pool wall tiles
Chrome corundum bricks were used as a replacement for corroded tank wall bricks, including electric bricks, in a cross-fired tank kiln. The tiles came into contact with the glass liquid immediately after installation, but no cracks occurred during the installation process. The kiln was shut down after 3 years of operation. There were only a few large erosions of 50mm at the liquid level. Glass companies that use chrome corundum for tiling have never seen any impact of tinting on the quality of the glass.
Use chrome corundum material to make key parts of the inner layer of the kiln
Refractory bricks based on chromium corundum oxide ceramic bonding have been used in various parts of the inner layer of glass furnaces for many years. The application scope of this refractory material involves the very critical inner parts of glass wool, mineral wool, and soda-lime vessel glass kilns. Such as the corners of the feeding end and the liquid hole as well as the inner layer of the entire kiln. Continuous improvements to this material have resulted in even better performance. RS refractory material manufacturers can produce various types of chromium corundum products with chromium oxide content from 10% to 70%. To extend the life of the pool furnace, research chromium corundum materials with corrosion resistance comparable to isostatically pressed products, and reduce costs.
Years of practical application of chromium corundum refractory materials have shown that its strong corrosion resistance and erosion characteristics fully meet the design requirements. In soda-lime glass furnaces, they protect key furnace parts very well and also enable the corrosion-resistant fiberglass furnace to have a furnace life of 4-5 years.
Chrome corundum bricks for garbage incinerators
Waste incinerator is a common thermal equipment in municipal waste treatment. According to different incineration methods, it can be divided into intermittent incinerators, grate incinerators, CAO incineration systems, fluidized bed incinerators, rotary kiln incinerators, etc. Among refractory materials for incinerators, refractory materials containing chromium oxide have good corrosion resistance. When the temperature is greater than 1250°C, chrome corundum bricks can be used as the lining of the incinerator.
The Al2O3 content in chromium corundum bricks used in garbage melting incinerators is 83.5%, and the Cr2O3 content is 9.3%. The bulk density is 3.09g/cm3, and the normal temperature compressive strength is 91.8MPa.
Abroad, the aggregate particle size of chrome corundum bricks used in garbage melting furnaces is less than 2.5mm, mainly corundum, and the dosage accounts for 20% to 30%. Chromium oxide is only 2%, while the chromium oxide content in fine powder is relatively high, around 5%. From the composition difference between aggregate and fine powder, it can be confirmed that the brick is sintered at medium temperature and the binder is phosphate.
Regarding chrome corundum bricks, Rongsheng Refractory Materials, as a professional refractory brick manufacturer, has complete quality testing standards and monitoring systems. Rongsheng adopts the double-three inspection method, strict self-inspection, random inspection, and re-inspection procedures. Ensure that each batch of refractory materials can meet the user’s standards so that customers can buy with confidence and use them with confidence.
Are chrome corundum bricks expensive? How much does a ton cost?
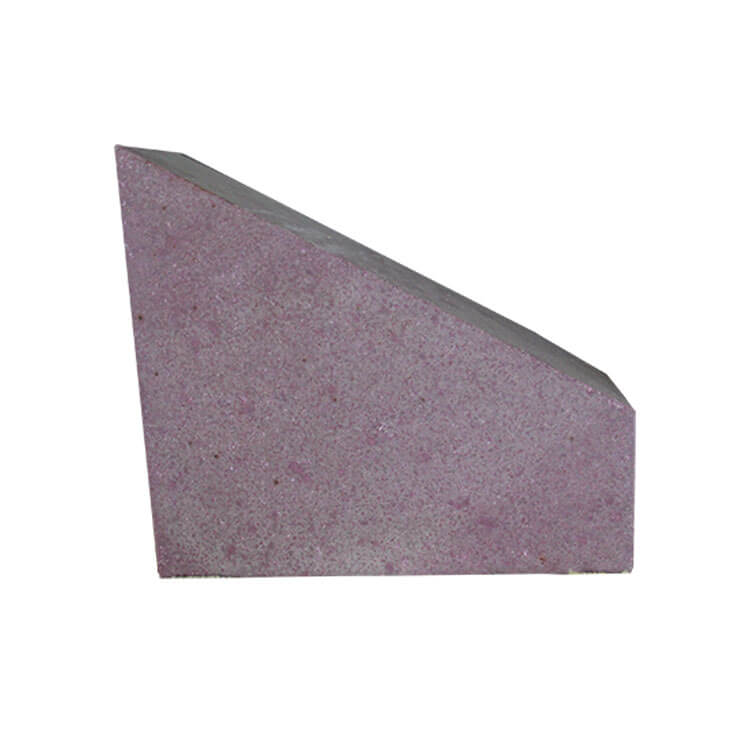
Chrome corundum brick is a special product with chromium added to the corundum brick. It has good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, impact resistance, and other properties. Prices vary based on market demand and differences in chromium content. Generally, the price of chromium corundum bricks with a chromium content of 5% to 10% is about 13,000 yuan/ton, while the price of chromium corundum bricks with a chromium content of 30% to 50% is more than 20,000 yuan/ton. The price of chrome corundum bricks is closely related to market demand. When market demand is high, prices will rise accordingly; when market demand is low, prices will fall. In addition, the difference in content is also a key factor affecting the price of chromium corundum bricks. The higher the chromium content, the higher the price.
In actual production, the price of chrome corundum bricks is also affected by other factors, such as production costs, production processes, sales channels, etc. The rising production costs, including raw material procurement costs, production equipment costs, labor costs, etc., also directly affect the price of chrome corundum bricks. In addition, the production process of chrome corundum bricks will also affect its price. High-end production technology will make the price of chrome corundum bricks higher. At the same time, different sales channels will also lead to differences in the price of chrome corundum bricks. The price purchased directly from the manufacturer may be lower than the price purchased from agents or dealers. Based on the above factors, the price of chrome corundum bricks is not only related to chromium content but also related to market demand, production cost, production technology, and sales channels. The prices of chrome corundum bricks of different specifications and quality will be different. If you need to purchase chrome corundum bricks, it is recommended to choose a reliable brand and channel for purchase after making multiple comparisons.
More Details