Since ceramic rollers operate under high temperatures and loads for a long time, various problems are prone to occur during the production process. Such as the middle break, the replacement roller burst, the roller head cracks, bending in the kiln, etc. Most of these problems are caused by the service life of the rollers, and some are caused by the quality of the product itself or improper operation. So, do you know what problems will occur when using ceramic rollers? What is the correct way to use ceramic rollers? Industrial ceramics factories will provide reference answers.
What are the Common Problems with Ceramic Rollers?
Common problems in the use of ceramic rollers are mostly caused by defects in the rollers.
1 middle break
The roller is broken horizontally, with neat fractures and loose cross-section, also called horizontal breaking. The main reasons for the breakage of the roller rod are as follows.
(1) The kiln firing temperature is too high. For example, the operating temperature of medium-temperature rollers is within 1000°C, the operating temperature of medium-high-temperature rollers is within 1200°C, and the operating temperature of high-temperature rollers is within 1250°C. If this extreme temperature is reached or exceeded, the phenomenon of roller breakage will increase significantly.
(2) The influence of roller load, span, and speed. When producing ceramic tiles or other products with larger specifications, the heavier the weight of the product, the larger the width of the kiln (more than 2.7m), and the larger the span of the rollers. The faster the roller rotates, the greater the chance of roller interruption.
(3) Improper selection of rollers. When producing ceramic tile products with specifications above 600mm×600mm, it is best to use a Φ50mm roller. To produce products of 800mm×800mm and above, it is best to use rollers with Φ60mm or Φ65mm specifications. The production of daily-use porcelain or other rare earth raw materials that are loaded and unloaded in the form of saggers or backing plates requires the high strength of the roller, so ultra-high temperature rollers should be selected.
(4) The roller rod is severely corroded. Since the roller rod has been running in the kiln for a long time and is affected by the kiln pressure, kiln atmosphere, and fuel-corrosive gas, the roller rod has a certain service life. Generally, the strength of the roller will gradually decrease after being used for more than two months, and interruptions may occur under load. The main manifestations of this type of broken rod are neat fracture, loose cross-section, and color on the surface of the cross-section.
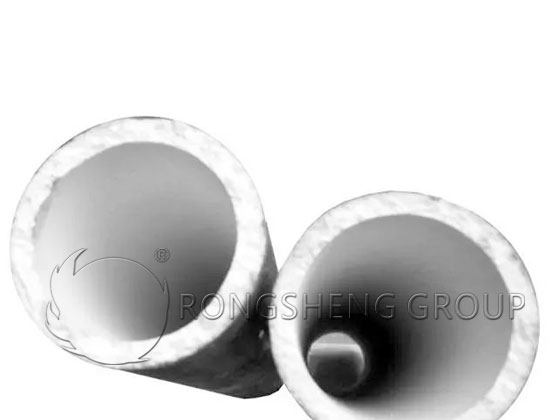

(5) The roller itself is not strong enough. If the new rod penetrates into the high-temperature area of the kiln and naturally breaks after a few days of operation, it is a quality problem with the product itself. This type of broken rod has neat fractures and loose cross-sections, but the surface of the cross-section is colorless.
2 The roller exploded when replacing it.
The main symptoms of explosion when changing the rod are crack lines along the length of the roller rod and two or more fractures. Or it may be broken, with uneven fractures and smooth cross-sections. The main reasons for the explosion are as follows.
(1) The rod replacement temperature is too high. The temperature for normal roller replacement is best controlled at 800~850℃ and should not be too high. At the same time, as the diameter and length of the roller rod increase, the surface area of the roller rod increases, and the thermal stability of the roller rod gradually becomes worse. During the process of changing from high temperature to normal temperature, the temperature inside and outside the roller rod is inconsistent, resulting in an explosion.
(2) Improper rod replacement operation. When pulling the rod, the red high-temperature part of the roller comes into contact with a good conductor of heat such as iron. During the cooling process, the contact point of the roller shrinks sharply, causing it to explode. If there are water stains on the ground where the roller is placed or if the roller is forced to cool with wind, it will also cause the roller to burst.
(3) The protective coating is not dry yet. The coated roller contains more crystal water and adsorbed water. The roller must be placed beside the kiln to fully dry before use. Otherwise, when entering the high-temperature area, the roller rod will burst due to the rapid evaporation of water.
(4) The roller rod is severely corroded. The rollers were corroded by corrosive gases in the kiln, causing obvious structural variations in the cross-section of the rollers (comparison of old and new rollers), or delamination in the cross-sections of the rollers. It is easy to burst, linearly crack, or break into several sections during the cooling process. The color of the surface of the eroded roller changes significantly.

(5) The adhesion of blank or glaze droplets on the surface of the roller rod is too serious so that the pores on the surface of the roller rod are blocked, the porosity changes and the inner and outer shrinkage is inconsistent during the cooling process, leading to an explosion. The roller bar after sticking the rake is shown in Figure 3.
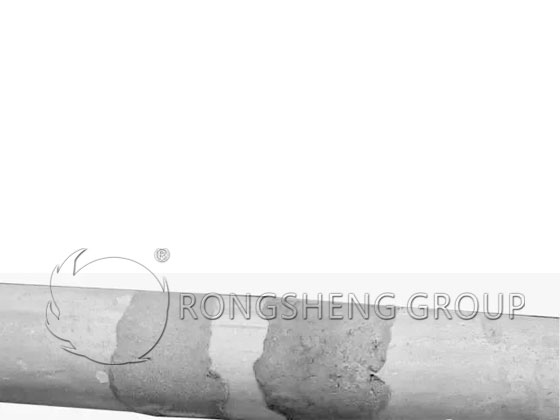

(6) Due to the poor thermal stability of the roller itself, the roller is prone to bursting when it is inserted into the high-temperature section of the kiln after preheating in the low-temperature section. The fracture of this type of broken rod is uneven, smooth, and colorless. See Figure 4.
3 The roller rod is broken and broken.
The main causes of roller cracks and broken ends are:
(1) The outer diameter of the roller rod does not match the inner diameter of the kiln transmission sleeve. The sleeve itself has tolerances, and the tolerance of a normal sleeve is 0~0.2mm. In actual production, there are problems such as the inner diameter of some sleeves being too small, so that the inserted roller rod is too tight and a broken head occurs.
(2) The kiln transmission sleeve is deformed due to inconsistent operation after the roller is inserted. Twist the roller rod and break the end. Deformation of the kiln wall or displacement of the kiln hole bricks can also lead to roller breakage.
(3) Excessive force when inserting the roller into the sleeve can easily cause the roller to crack.
(4) The roller itself has dark cracks. After being inserted into the kiln, cracks will appear under high-temperature conditions, and breakage will gradually occur after the sleeve is inserted. The split head stick is shown in Figure 5.
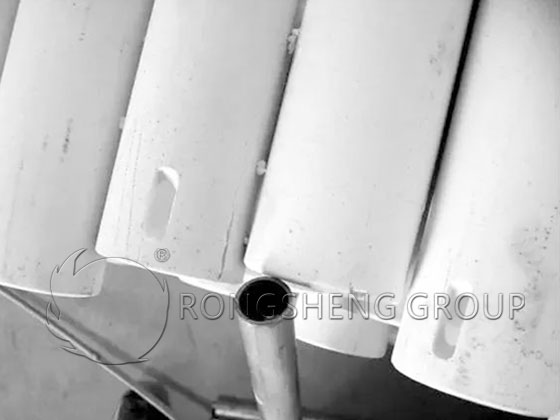

4 Bending deformation
There is a certain correlation between the bending deformation of the roller and the interruption of the roller. The main reasons for the bending deformation are:
(1) Because the current firing cycle of ceramic products is relatively certain. When the firing cycle is constant, the longer the kiln, the wider the internal width, the faster the roller rotation speed, the higher the firing temperature, and the easier it is for the roller rod to undergo high-temperature bending deformation.
(2) Due to the influence of the quenching air curtain in the quenching zone of the kiln, the bricks need to be cooled from the highest temperature to 600-700°C in a short period of time. The temperature difference between the upper and lower rollers in this area is quite large, and the rollers are prone to bending.
(3) It is worth noting that if individual rollers of different batches of products are bent and deformed under basically the same conditions of use, it should be caused by quality problems of the roller itself.
How to use ceramic rollers reasonably?
- The inner cavities at both ends of the newly purchased ceramic roller should be filled with 100mm long ceramic loose cotton and a mark should be made on one end of the roller. Use it once in the kiln and mark it once to determine the length of use.
- The surface should be coated with a protective coating before entering the kiln. The sizing length is generally 100mm longer than the effective width in the kiln, and the thickness is between 0.8 and 1.2mm. Sizing can be done in two steps, and the surface must be cleaned before sizing.
- Ceramic rollers should be preheated and dried for 24 hours before being loaded into the kiln.
- After applying the base paint, the dirty roller should be replaced in time. Generally, it is better to cool down to 800℃ and replace them centrally.
- Whether loading or unloading the kiln, it must be as fast as possible. The extracted ceramic roller must adopt the correct cooling method to prevent “wind shock” caused by local rapid cooling.
- The extracted product must be cooled using the correct method. Do not place it directly on the ground. Generally, a mechanical rotating stand and a cold roller are used. After exploration, the vertical suspension cooling method saves people and effort, and the effect is good.
- After the replaced dirty ceramic roller is polished, its straightness, diameter, etc. must be carefully checked for reuse.
- Choose a reasonable blank formula and brick primer. The surface coating liquid can reduce the chemical corrosion of the body and reduce the occurrence of roller breakage accidents.
To purchase high-quality ceramic rollers, please choose a strong ceramic product manufacturer.